There are two types of pregnancy tests that can be performed in a laboratory: blood and urine tests. Both tests measure the hormone hCG, or human chorionic gonadotropin. The hCG hormone is produced by the placenta after the embryo implants into the uterus. A positive pregnancy test result is achieved when this hormone is detected.
Urine Pregnancy Test
For a urine pregnancy test, urine is collected in a sterile container, and the test stick is dipped into it. Another method involves wetting the middle section of the test stick while urinating. After a short wait, the presence or absence of pregnancy is determined based on color changes on the test stick. Tests conducted with the first morning urine tend to yield more reliable results. The outcome of the pregnancy test is interpreted based on the appearance of lines indicating color change. A single line means the test is negative, while two lines indicate a positive result. Although home pregnancy tests are generally accurate, women suspecting pregnancy are advised to consult a healthcare provider.
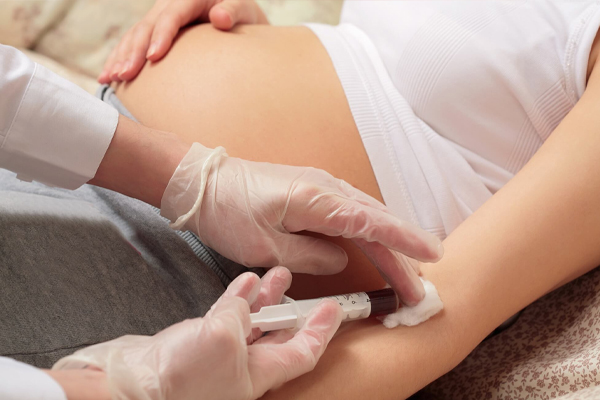
Blood Pregnancy Test
A blood pregnancy test is conducted by analyzing blood drawn from a woman referred to the laboratory due to pregnancy suspicion. The test detects the presence of the hCG hormone in the blood, and its presence confirms a positive result. A blood pregnancy test can provide results 7–12 days earlier than a urine test. Additionally, blood values can be examined for health assessments. Compared to urine tests, blood tests are more expensive, require a laboratory setting, and take longer to deliver results.
When to Take a Pregnancy Test?
A missed menstrual period is a significant reason to take a pregnancy test. If conducted at home, the pregnancy test is typically a urine test. A positive urine test indicates pregnancy. However, whether the pregnancy is intrauterine or abnormal can only be determined via ultrasound. These tests, which are generally 97% accurate, may yield misleading results if performed too early. For instance, you might be pregnant even if the test shows a negative result. In such cases, the test should be repeated a few days later if menstruation still has not started. A negative test result does not necessarily mean you are not pregnant—it may be defective or performed too early. For women with regular menstrual cycles, the test result will be positive about two weeks after fertilization and 1–2 days after the expected menstruation date. For those with irregular cycles, this period may be longer.
Symptoms of Pregnancy
Pregnancy usually presents with similar symptoms in most women. Fatigue, increased vaginal discharge, nausea, breast tenderness, delayed menstruation, and darkening of the nipple area are the most common symptoms.
Breast Tenderness
Increased visibility of veins on the breasts, darkening of the nipples, and painful, sensitive breasts may be among the early signs of pregnancy.
Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are among the most common symptoms of pregnancy. These typically begin around the sixth week and are more intense in the mornings. The cause is the body adjusting to changes in hormone levels.
Emotional Changes
Emotional changes, such as increased sensitivity, irritability, and mood swings, are normal due to hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy.
Dizziness
Frequent dizziness in early pregnancy is a result of insufficient blood flow caused by the pressure exerted by the growing uterus.
Food Cravings
Food cravings are a hallmark of pregnancy, though not all pregnancies feature this symptom. It is especially common during the first trimester.
Spotting
Light spotting, often referred to as implantation bleeding, is one of the most definitive signs of pregnancy. It is not as heavy as a normal menstrual flow.
Cramps
Cramps resembling menstrual pain may indicate pregnancy as the uterus expands to accommodate the growing fetus.
Frequent Urination
Frequent urination is another potential sign of pregnancy, as the body produces extra fluids, altering bladder function. Additionally, dark-colored urine may indicate pregnancy.
Shortness of Breath
The growing fetus in the womb requires oxygen, which can increase the mother’s oxygen needs and lead to shortness of breath.
Constipation
Increased progesterone production during pregnancy can affect the digestive system, causing bloating and constipation.
Sensitivity to Smells
During pregnancy, the sense of smell sharpens, making pregnant women more sensitive to even faint odors. Strong scents, such as cigarette smoke or perfume, can intensify nausea.
Changes in Taste Perception
One early sign of pregnancy is a change in taste perception. Pregnant women often report heightened sensitivity to flavors.
Missed Period
If menstruation does not occur as expected, there is a high likelihood of pregnancy. The first and most definitive sign of pregnancy is a missed period. Additionally, lighter-than-normal bleeding may also indicate pregnancy.
Fatigue and Weakness
Fatigue and weakness during pregnancy can occur due to increased hormone levels in the body. This symptom usually lasts through the first trimester and gradually fades away.